The Merge (Part II) | DeFi Download
Your Trusted Source for 101s, Project Announcements, and Tokenomics Tutorials.
Dear Bankless Nation 🏴,
The Merge is here! The Merge is here!
Unlike when we wrote those words two weeks ago, today the Merge is here. In fact, it’s not just here, it happened! And it was a resounding success.
At approximately 7am UTC on September 15, 2022, Ethereum became a blockchain validated by a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism. This transition away from proof-of-work to a less energy intensive and more scalable framework was well over five years in the making, but it happened in just an instant. Or to paraphrase a popular saying, the Merge was an overnight success five years in the making.
The change to proof-of-stake is about so much more than energy conservation, although it’s worth restating that an Ethereum network that consumes 99.95% less energy and is ESG compliant enables many of the world’s largest investment houses and mindful investors to take a second look at ether. No, the true power in the transition from proof-of-work to proof-of-stake is that it provides both the engine and the fuel to power what’s to come: a solution to the Scalability Trilemma, a blockchain that is secure, scalable, and decentralized.
But we’re saving the Ethereum Roadmap for the final issue of our Merge Trifecta. In this issue of the DeFi Download, we’ll review the Merge mechanics and highlight issues with consensus and execution layer client diversity and staking service centralization (it’s very important stuff!!), compare liquid staking tokens and do a deep dive into Lido and Rocket Pool, provide an accessible guide to ETH staking tactics, and conclude with a roundup of tweets and DeFi news.
It’s not just that Ethereum had a successful Merge; it’s that in many ways we all did. We saw what can happen when a small group of dedicated builders set out to solve hard problems. And solving hard problems is why many of us are here. So let’s tip our hats to the core devs, catch up with where we are with Ethereum, and get back to work. Thanks for being on this journey with us.
Contributors: BanklessDAO Writers Guild (Austin Foss, Elemental, helloashpreet, Hiro Kennelly, oxdog, siddhearta, Yiki.eth, Teeleroo, Jake and Stake)

This is the official newsletter of BanklessDAO. To unsubscribe, edit your settings.
🙏 Thanks to our Sponsor

The DeFi Download Guide to the Merge (Part II)

First we begin with the mechanics of the Merge and introduce the importance of staking diversity and client diversity. Afterwards, we break down the tokenomics of liquid staking derivatives, dig into two of the most popular staking services, and show you how to stake your ETH. The Merge (Part II) of the DeFi Download Guide to the Merge will set your foundation for blockchains.
How the Merge Happens
Author: oxdog
Long Anticipated
From its launch in 2015, Ethereum was intended to switch from proof-of-work (PoW) to proof-of-stake (PoS) within a year. As it turned out, this was a more complex task than anticipated and led researchers down a multi-year rabbit hole.
A plan with two phases was initiated to accelerate the switch to PoS. The first phase was the launch of the Beacon chain in 2020, and the second phase is the upcoming Merge. To understand the transition of the consensus mechanism from PoW to PoS, we have to look at two layers of the blockchain:the execution layer and the consensus layer.
The execution layer is what the user experiences. It is the transactions and payloads that get included in a block. The consensus layer is how miners - later in PoS validators - agree on what data is correct across the decentralized network of Ethereum. To have a working blockchain, both layers need to work in tandem. Because the layers are separate, they can be developed independently, allowing the Beacon Chain to launch and start developing on the PoS consensus client earlier.
The Transition to PoS
Thus far, the Beacon Chain is a sidechain that runs besides Ethereum and does not produce any blocks. It provides an environment where the PoS consensus client can be developed without impacting the PoW chain. Launching the Beacon Chain avoided dependencies on Ethereum PoW, which would have slowed down development. It also provided time for people to start running validators and to stake. Currently, there are around 400k validators and 13M ETH staked.
In PoW Ethereum, the surrounding PoW consensus layers protect the execution layer. With the merge, the Beacon Chain replaces this surrounding shell with the PoS consensus layer. This transition happens from one block to the next without any interruption. The exact block where this will happen is determined by a terminating condition that all network clients have agreed upon. This condition is the Total Terminal Difficulty (TTD).
TTD vs. Block Height
In PoW, new blocks are mined with varying difficulty. The Total Difficulty is the sum of difficulties from all blocks. The Total Terminal Difficulty is the value at which the Merge happens.
For regular updates in Ethereum, like implementing a new feature, the point in time is determined by the block height, which refers to the total count of blocks in the chain. With every block mined, the height gets increased by one.
This is the first time TTD is used to determine a network upgrade. If block height would have set the Merge, malicious actors could have mined multiple low-difficulty blocks to cause confusion among the clients that run the network. TTD prevents this attack since the chain simply continues on the block with the highest TTD.
Clients
To run a full node in the PoS network, two clients are needed to run the two layers: an execution client and a consensus client. An essential role in Ethereum is client diversity, which means there are multiple implementations for execution and consensus clients, each developed by a different team.
Popular execution clients are Geth, Erigon, or Nethermind; popular consensus clients are Lighthouse, Prysm, or Teku. These clients can be combined freely with each other via the Engine API. One might choose to connect Geth with Lighthouse, and another might run Erigon with Teku. With four execution clients and five consensus clients, there are a total of 20 different combinations. There must be multiple clients because if a bug is found in a single client, its failure does not significantly impact the network, strengthening the stability of the network.

Staking Service Provider and Client Diversity
Author: Yiki.eth
One of the most important things regarding the Merge is the diversity of both staking services and clients. Both are crucial to the security of the Ethereum network.
According to Dune Analytics, by September 10, there is more than 13 million ETH deposited on Beacon Chain. 30% of the market share is taken up by Lido, a liquid staking service provider, while the big central exchanges, Coinbase, Kraken, Binance are among the other biggest depositors, taking up 14.5%, 8.3% and 6.6% market share.
Client Diversity
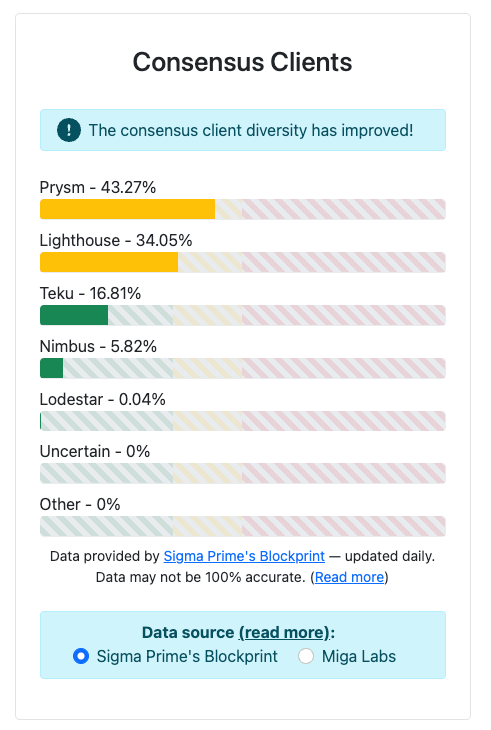
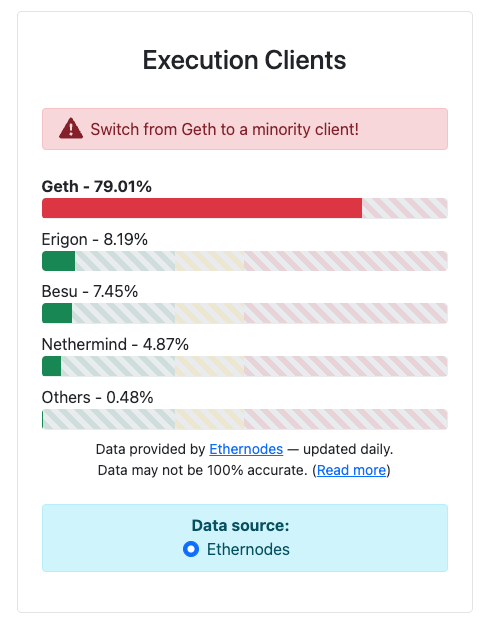
There are more than 42,000 validators on the Beacon Chain. The diversity of the software clients they choose to run is also a security concern. The Ethereum protocol supports multiple clients in order to increase the robustness of the network. If one client has a bug, it’s not fatal to the system, but the risk is higher when clients compose a large majority of network.
As a whole, the network is in danger when a single client has a 33% share of the network. A bug in this majority client can cause finalization problems. At the time of writing, Prysm and Lighthouse have over 33% of the consensus client share.
The situation is even more dire with execution clients. Geth has a whopping 79% share.
Having a client representing more than ⅓ of the total staked ether is problematic, extremely multiplying the vulnerability of the Ethereum chain. When the proportion of one single client is up to ⅔, the security of the chain becomes totally in trouble, which can result in finalizing incorrect information and cementing it forever on Ethereum.
If you’re running a node, please consider switching to a minority client in order to improve the health of the chain!
Liquid Staking Tokens
Author: Elemental
All staked ETH will remain locked in the Beacon Chain until after the forthcoming Shanghai upgrade—expected to occur 6 to 12 months following the Merge. This means that regardless of whether you’re running your own node or staking ETH through a third-party, you won’t be able to access your staked ETH until well into the future. In addition, once withdrawals are enabled, there will be a queue that could delay them for hours or even weeks.
Locking up capital for such a long time without the ability to withdraw, sell, or use it in DeFi is a tough sell for a lot of crypto investors. To overcome these drawbacks, staking providers developed derivative liquid staking tokens that allow stakers to sell, transfer, and use their staked ETH positions as collateral in DeFi. These tokens are readily tradable on major DEXs, which is what makes them liquid.
Let’s take a look at the two types of liquid staking tokens: rebase tokens and wrapped tokens.
Rebase Tokens Rebase tokens or “elastic supply tokens” follow a model pioneered by Aave’s AToken design. These derivative tokens are pegged 1:1 to the underlying staked assets. Token holders’ balances are “rebased” daily to include new staking rewards or penalties.
Lido’s stETH is an example of a rebase token. If you stake 1 ETH with Lido, you’ll receive 1 stETH token. Every day at 12 PM UTC, your wallet balance of stETH will adjust to a new amount that includes the previous day’s net rewards and/or penalties earned by your staked ETH principal. Lido’s staking rewards rates are variable. Currently stETH holders are earning around 3.8% APR, which per day is:
1 stETH x 3.8% = .038 stETH/year or .000104 stETH daily reward
So, on a typical day before the Merge, you would see your balance of stETH increase by .000104 stETH for each stETH token you hold.
Note that some jurisdictions may consider every daily account rebase adjustment to be a taxable event, which could affect the tax rate applied to earned staking rewards.
Pros:
Simple 1:1 exchange rate between liquid staking token and staked ETH on the platform
Up-to-date token and reward balances
Tradable on decentralized exchanges
Works with some DeFi protocols
Cons:
Not fully ERC-20 compliant
Not compatible with all DeFi protocols
Some jurisdictions may consider daily rebases to be taxable events
AMM liquidity pool imbalances can cause tokens to “lose peg” and not exchange at 1:1 with ETH on DEXs
Wrapped Tokens
Wrapped liquid staking tokens follow the cToken model developed by Compound. These tokens don’t exchange 1:1 with the staked asset. Instead, they use a floating conversion rate that accounts for rewards, penalties, and fees accrued over time; and factors in wrapping and unwrapping activity that affects the token supply.
Rocket Pool’s rETH is an example of a wrapped token. As of this writing, the conversion rate for rETH tokens is 1 rETH = 1.03699 ETH. Put another way, 1 rETH represents 1 ETH token plus .03699 ETH in staking rewards that the token has earned to date. This conversion rate will steadily increase over time as each rETH token gathers more rewards.
Once staking withdrawals are enabled on the Beacon Chain, wrapped staking tokens can ultimately be unwrapped and burned to return the staked ETH plus accumulated ETH rewards to stakers.
However, in the case of rETH, there may be little need to unwrap and burn the tokens since they should be readily exchangeable on DEXs for a similar amount of ETH. As long as DEXs have sufficient token liquidity, the exchange rate for rETH to ETH pair should remain close to the token’s conversion rate. rETH holders can also exchange their tokens for ETH on the Rocket Pool portal.
Pros:
ERC-20 compliant
Tradable on decentralized exchanges
Greater composability and compatibility with DeFi protocols
No taxable events from rebasing
Cons:
Difficult to understand how rewards accrue
Hard to track daily staking rewards performance
Leading Liquid Staking Tokens for ETH
Staking Protocols: Lido
Author: Austin Foss
Lido Finance Staking
Lido Finance was the first decentralised staking service for Ethereum. It was introduced on October 15, a month and half before the staking contract was open to the public on December 1st.
In the new proof of stake (PoS) paradigm the barrier to entry is not set by a hardware requirement investment, simply a modest capital investment of 32 ETH; ‘modest’. When introduced this was approximately “$11,744.32” USD, at today’s prices this ranges from $48,000 to $64,000 USD and is only expected to continue increasing. For almost everyone this is still beyond reach so it makes sense that the counterpart of a mining pool would be created for the PoS model and Lido intended to be the first.
While it was always expected exchanges and other companies would launch their own staking services to fill the same niche, Lido was the first to provide a decentralised service, launching on December 28.
Lido Protocol Pieces
To make Lido a decentralised protocol the following components need to be pieced together:
Smart Contracts
Node Operators
Oracle Operators
Staked ETH derivative ERC20 token, stETH, & its wrapped counterpart, wstETH
Lido DAO, governed by LDO ERC20 token holders
Deposit Security Committee; originally seven Node Operators designated as guardians
To get the protocol started the first step in the process is to have a validator client online and ready to accept the crowd sourced deposits. A prospective node operator makes their application to the DAO and once approved proceeds with the remaining steps to set up their validator(s). Second, stakers pool their ETH with the Lido protocol in a 1:1 exchange for the stETH derivative token. As new node operators add more unused validators to the protocol chunks of 32 ETH are submitted to the deposit contract in sequence of the non-used validators.
As part of the protocol there is a 10% fee owed to the Lido “treasury, insurance fund and Node Operators.” This fee currently comes from the consensus rewards on the beacon chain and will soon include the execution layer rewards from transaction priority fees and MEV derived value.
If the 1:1 ratio of ETH:stETH in issuance is to remain constant, more stETH must be minted and added to the balance of each stETH holder. This is accomplished by a rebase mechanism, the amount of each rebase is determined by the oracle operators each epoch.
Lido’s Degree of Decentralisation
Lido’s DAO plays several key functions in the protocol. First and foremost the DAO selects new and trustworthy node operators to run the protocol’s validators from a pool of applications submitted on chain. Lido’s DAO has control over various “levers” within the protocol such as:
Burning stETH after ETH has been slashed
Offsetting slashed ETH to maintain the ETH:stETH ration at a 1:1 rate is done by protocol voting
The protocol fee and it’s distribution
Calling the setFee() function changes the current 10% fee of staking rewards
Calling the setFeeDistribution() function changes the proportions sent to each benefiting group. Currently:
Node Operators: 5%
Treasury: 5%
Insurance Fund: 0%
Staking rate limiting
Due to the length of the post-merge staking queue having an excess amount of stakers would negatively impact the APR for current stETH holders. This allows the DAO to limit these effects until more of their validators can come online.
One last function performed by the DAO is to approve extra funding to secure and develop the protocol such as research grants, payout rewards for bug bounties, and add features.
Initial distribution of the LDO token looked like this in January 2021:
DAO treasury - 36.32%
Investors - 22.18%
Validators and signature holders - 6.5%
Initial Lido developers - 20%
Founders and future employees - 15%
Of the founders and investors who hold these tokens include a range of VC funds including “Stani Kulechov of Aave, Banteg of Yearn, Will Harborne of Deversifi, Julien Bouteloup of Stake Capital and Kain Warwick of Synthetix.” Founder tokens were locked for 1 year until December 17, 2021, and have undergone a vesting period that will end one year later; what seems to be approximately 3 months after the merge.
Finally the last piece of the puzzle is the Deposit Security Committee whose purpose is to prevent malicious node operators from front running a deposit such that the operators “effectively [get] control over 32 ETH from Lido.” This committee is a group of six node operators and the Lido development team. A process for decentralising this committee’s membership has not yet been defined but it is stated in the documentation that “the rest of the node operators can also participate via testnet and gradually get pulled into mainnet.”
Tokenomics & DeFi
Due to the effects of the rebasing mechanic stETH cannot be used in many DeFi protocols, necessitating the existence of its wrapped counterpart. Rebased rewards are only accounted for on wstETH transfers and unwrapping
DeFi integration for (w)stETH include:
stETH collateral asset on AAVE v2 market on Ethereum mainnet.
wstETH is listed as collateral asset on Maker.
steCRV (the Curve stETH/ETH LP token) is listed as collateral asset on Maker.
Strategies for Lido liquidity token derivatives are live on yearn and Harvest Finance.
Risks
One of the potential risks in the Lido protocol is in the degree of centralization in the DAO. With more than 50% of the total LDO supply initially being distributed to founders, investors, and employees, while unclear if this could be exploited it is something to keep in mind. At the time of writing Etherscan reports that more than 20,000 individual wallets hold the governance token—it seems distribution has spread out significantly beyond the original allocation.
Smart contracts risk is ever-present in DeFi, and Lido is no exception. If there is a bug vulnerability in the contracts, it could be exploited by a malicious actor. The centralised Deposit Security Committee was created to mitigate this risk.
One thing to note is that the rebase rewards earned on stETH can be considered taxable events, depending on where you live. Whether holding the wstETH counterpart may protect you from this headache, but this would be your responsibility to determine.
Last, but the most apparent, is validator slashing. Node operators, while approved and vetted by the DAO before being assigned the required 32 ETH from the pooled funds, could still experience problems. Node operators could go offline for any number of reasons, their choice of individual clients (lighthouse, geth, prysm, etc.) could experience bugs, etc. The DAO is responsible for managing slashing incidents through their “insurance policy”; a mechanism of burning stETH to maintain the 1:1 stETH:ETH supply ratio.
Centralisation of Ether staked in Lido also serves a risk to the Ethereum ecosystem itself, though this is not a direct risk for Lido. Holding just over 30% of the total staked ETH on the beacon chain has also caused concerns surrounding the Geth client dominance at the execution layer.
Most of the validators operating on behalf of Lido stakers are independent so coordinating to attack the consensus layer is exceedingly unlikely if not impossible. Still, this could cause unforeseen problems if Lido is hacked.
By the Numbers
4,161,000 ETH Staked
182,000 Stakers
75,000 Unique Depositors
stETH/ETH = ~0.9715
~3.8% APR
20,000 LDO holders
Rocket Pool
Author: Jake and Stake
Launched to mainnet on on November 9th, 2021, Rocket Pool’s goal is to further decentralize Ethereum staking. The primary value proposition Rocket Pool offers users is that it allows anyone to participate in staking without the 32 ETH capital requirement.
Rocket Pool divides users into 2 categories:
Users that want to access staked ETH rewards through their derivative (rETH).
Users that want to stake ETH and run a validating node.
Rocket Pool is a staking derivative protocol that allows users to swap their Ether (ETH) for rETH from the RP contracts or any number of exchanges. rETH holders get interest on their ETH, can swap rETH for other assets, and use rETH in several DeFi protocols:
In order to run a full validating node, users must have 32 ETH staked, Rocket Pool serves users that have less than 32 ETH by allowing them to buy the derivative or run a Rocket Pool node.
With Rocket Pool, running a node only requires a minimum of 16 ETH per validator vs 32 ETH outside of the protocol.
Rocket Pool node operators supply 16 ETH to run a pool, with the other half of the requirement coming from the Rocket Pool contract. Users that don’t want to run a node can deposit ETH into the Rocket Pool contract and get staked ETH rewards. The sum of rewards are shared amongst rETH holders with operators receiving a commission in exchange for running a node.
Permissionless: No whitelist to acquire rETH or run a node. (No KYC —> very decentralized). Even centralized entities like Bison Trails or Gemini could use Rocket Pool to create nodes or purchase rETH.
Trustless: Smart contracts are publicly verifiable. Very few trust assumptions making it perfect as a DeFi building block.
Diversity: Use any number of core Ethereum clients (execution and consensus).
Highly aligned with Ethereum.
Rocket pool serves as a two-sided marketplace for node operators and liquid staking derivative buyers. This market will create creating additional competition for staking providers.
The core premise behind a protocol is to ensure the network is not beholden to any one party. This is a principle directly linked to Ethereum and Proof-of-Stake itself, and a mindset used at every stage of the process as we develop Rocket Pool for its upcoming launch. - David Rugendyke (Rocket Pool Co-Founder and CTO)
Aligning with Ethereum values, Rocket Pool wants to be as trustless, permissionless, and self-sovereign as possible.
Rocket Pool is a protocol meaning anyone can run the software and spin up a node. Rocket Pool is even available to centralized staking providers who want to earn additional commission and improve the decentralization of the network.
Community (Lido vs Rocket Pool)
Node operators focused on:
MEV Extraction
Efficient Staking architecture
Protocol updates
rETH token holders focused on:
Increasing liquidity
Increasing utility
These parties work together to improve the protocol and give everyone value (token price, utility, and rewards).
There are two different DAOs in the Rocket Pool ecosystem:
The Protocol DAO is responsible for RPL inflation, RPL rewards for the DAOs & Node Operators, RPL auctions, Node staking amounts, network fees, and deposit amounts of ETH for rETH (min/max).
The Oracle DAO is composed of oracle nodes.
Tokenomics
Staking is going to be very important in a post-Merge world. Staking yield goes down as risk goes down.
Liquid staking tokens are productive assets and provide much more value than vanilla ETH.
Value accruing vs rebasing tokens. More tax advantageous and easier to integrate on mainnet and other L2s.
Rebasing
Lido’s stETH is pegged 1-1 to ETH and holders get a small dividend in stETH. Doing rebasing on L2s is complex and harder to implement.
Non-Rebasing
You don’t receive more units, but the price of the token goes up compared to ETH. Composable, easier to integrate, and the receiving of rewards is a non-taxable event. The lack of tax liability improves the “real yield” of your investment.
Assuming the tokens have the same yield, rewards are the same:
Rebasing: 1.0 stETH + (1.0 * .05) stETH = 1.05 stETH
Non-Rebasing: rETH/ETH = 1.05 rETH
$RPL
Node operators must stake a minimum of 10% of the MiniPool's value in ETH (i.e. 1.6 ETH) in RPL in order to create a MiniPool. The RPL acts as insurance should the node behave maliciously, while compliant nodes are rewarded with $RPL emissions.
Utility:
Governance
Serve as insurance for users that stake with rETH. If the RPL token is auctioned if/when the staker is removed from the network.
Node operators must buy and stake at least RPL in order to create a pool. (10% of the 16 ETH required denominated in RPL).
Supply Dynamics
RPL tokens inflate at a rate of 5%. Of which, 70% is sent to node operators 30% is sent to the Oracle DAO (oDAO). These are Oracle Node operators that relay information from the beacon chain to the contracts in the PoW Ethereum execution layer.
DeFi
Integrations are coming. rETH launched over 10 months ago giving it more Lindy and protocols are noticing:
Maker
Aave
Curve
Balancer
Bancor
Subgraph
Alchemix
Ribbon
Uniswap
Convex
Ribbon
Liquidity incentives will grow the protocol a lot. Free, boosted yield.
Risks
Worst-case scenario: Mass slashing event where validators are taken offline. Ethereum was built for home stakers to safely run nodes, making Rocket Pool risk similar to the protocol as a whole.
rETH is overcollateralized, meaning there are more assets serving as collateral than rETH issued. rETH is backed 1-1 with the additional 10% of RPL staked. Thus rETH holders are largely protected from validator misbehavior, but if there is a large slashing event, operators must pay the costs of node failure.
Penalties are fairly marginal, except in the case of finalization disputes.
Catastrophic events: the network goes down, multiple bugs in multiple clients, and Ethereum core developers can’t achieve consensus on how to solve the problem.
For node operators: If you are penalized by the staking protocol, and you end the round with less than 16 ETH your collateral will be sold for ETH at auction and the proceeds given back to the protocol to compensate for the missing ETH. Penalties can be high for losing funds.
If this isn’t enough to cover the lost funds, the value of the rETH token will be reduced to reflect the network’s performance.
For example, if a node leaves the network with 28 ETH, the operator retains 12 ETH, the network retains 16 ETH - all loss is on the operator. If a node leaves with 15 ETH, the network retains 16 ETH and the operator makes up the missing 1 ETH through the loss of RPL. If the node leaves with 10 ETH, and there is only 1.6 ETH-worth of RPL from the original bond, the network retains 11.6 ETH, and the loss of 4.4 ETH (16 - 10 + 1.6) is spread across the network.
Running a Node
You’ll make a greater return.
Node runners allow rETH holders to contribute to the robustness of the network.
Execution Node
Anyone can run an execution node. Rocket pool has software that allow users to run one which is constantly updated.
Oracle Node
The oracle nodes bridge the gap between the Beacon Chain and the smart contracts in PoW Ethereum’s execution client. They’re responsible for:
Monitoring the performance of Minipools (validators) and calculate the correct exchange rate of rETH and ETH.
Determining the ratio of RPL/ETH to distribute RPL rewards correctly.
Marking validators as exited/withdrawn
Making sure the protocol is live, staking as much ETH as possible to generate yield on deposited ETH
The oracle network is composed of Rocket Pool community members and work together as a network, voting on each statement. All oracle data requires >= 51% of members to agree.
Membership at the time of writing is granted upon invitation by an existing member. Following an invitation and a sizable amount of RPL as collateral, existing members must vote on whether to include the invited node.
Members can be kicked out of the network if they are found to be reporting bad balances, regularly going offline, or performing some other malicious behavior. They may also have some of their RPL penalized.
These oracle nodes are paid using 15% of RPL token emissions.
Validating Node
Solo validators must raise 32 ETH of collateral, but Rocket Pool only requires 16 ETH and 1 ETH worth of RPL. Eventually, Rocket Pool plans to allow users to be node operators with only 4 ETH.
Operators earn:
Interest on their own 16 ETH (ETH issued, tips, and MEV)
Node operator commission on the other 16 ETH (15%)
Low ETH-bonded mini-pool (8 ETH deposit example).
Interest on their own 8 ETH (ETH issued, tips, and MEV)
Node operator commission on the other 24 ETH (15%)
Rocket Pool node operators receive a commission that is actually variable. If a lot of ETH that needs to be staked and there aren’t many node operators available, the commission rate will rise. Currently, the minimum commission is 5% of rewards earned and the maximum is 20%.
5% Ethereum Yield & 15% commission fee
1 Node(s) * (16 * (1.05)) + (16 * (0.05) * (0.15)) = 16.92 ETH (5.75% return)
2 Node(s) * (8 * (1.05)) + (24 * (0.05) * (0.15))) = 16.98 ETH (6.12% return)
4 Node(s) * (4 * (1.05)) + (28 * (0.05) * (0.15))) = 17.01 ETH (6.31% return)
10% Ethereum Yield & 15% commission fee
1 Node(s) * (16 * (1.10)) + (16 * (0.10) * (0.15)) = 17.84 ETH (11.5% return)
2 Node(s) * (8 * (1.10)) + (24 * (0.10) * (0.15))) = 17.96 ETH (12.25% return)
4 Node(s) * (4 * (1.10)) + (28 * (0.10) * (0.15))) = 18.02 ETH (12.6% return)
The Redstone Update
New Rewards System
Users can let their rewards accumulate as they wait to claim them. Users have the option to claim multiple intervals at once making it more gas-cost-effective.
Users can re-stake some or all of their RPL rewards in order to increase yield and reduce gas requirements. Rocket Pool plans to allow users to claim their rewards on L2 networks.
If you are below 10% RPL collateral at the time of the snapshot, you will not be eligible for rewards for that snapshot. […] You must be above 10% collateral at the time of a snapshot in order to receive rewards for that period.
Smoothing Pool: An opt-in feature that allows nodes to share block proposer rewards with each other. The chance that your validator will get to propose a block is random, so sharing the proposer rewards between all of the network’s participants will create a steady stream of income.
The node operator's total share is determined by the average commission of every minipool in every node opted into the Smoothing Pool.
Option for validators to share the rewards with each other and distribute it equally based upon the contributions of pool operators. MEV is akin to a lottery, but the smoothing pool allows operators to increase their share of received MEV.
By the Numbers (Stats)
Total ETH Staked: 195,063
Active Nodes: 1,369
rETH/ETH = 1.0364
Wallets with >10 RPL Tokens: 1,270
RPL staked: 6,481,437
~3.61% APR
Source: https://dune.com/NDGcrypto/Rocket-Pool-rETH-and-Nodes
ETH Staking Tactics
Author: Hiro Kennelly

There are a number of ways to gain exposure to the Merge and the opportunities afforded by the shift to a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, but perhaps the most satisfying is to earn yield by staking ETH. After all, you’re not just earning interest on your digital assets, you are also helping to secure the Ethereum network.
Stakers who run nodes are also known as validators, because they propose and validate new blocks, which enables them to earn yield on their ETH. This yield primarily comes from block rewards and tips/bribes paid to validators to order transactions in a certain way. The current staking yield is about 5%, but many estimate that staking yield may average 10% long term.
And here’s the great thing: you don’t have to be a validator to participate in ETH staking or to earn staking rewards. With the Merge complete, now is a great time to get in the ETH staking game.
There are four main ways to stake ETH:
Centralized exchanges
ETH derivatives / liquid staking tokens
Running a partial node through Rocket Pool
Running a full node
The list above ranks these yield-generating methods from basic to complex, and we’ll run through each option so you’ll have a sense of which tactics you want to employ to start earning yield on your ETH.Important note! If you lock your ETH into a staking contract, you will not be able to directly withdraw it before the Shanghai upgrade, which is expected to occur six months after the Merge.
Tactic #1: Stake ETH on Centralized Exchanges
The simplest way to earn yield on your ETH is to stake it with a centralized exchange. These exchanges stake your ETH for you, passing on some of the yield generated through validation. Most major centralized exchanges offer similar ETH staking programs, but as an example, to stake on Coinbase, you follow these steps:
Hold ETH on Coinbase
Click on ETH
Find the ‘Stake now’ button
Read disclaimers
Choose the amount to stake
Complete transaction.
By way of platform comparison, Coinbase is currently offering 3.25% while Binance is offering 6%.
With staked ETH, you’d normally have to wait until the Shanghai upgrade to withdraw it. But since Coinbase introduced cbETH, its own ETH staking derivative (that we’ll cover below), you can swap your staked ETH for cbETH and then for ETH. cbETH is slightly depegged, so you’ll lose some ETH in the process, but if you’re really motivated to regain control over your ETH, this can be a great way to do it.
While staking through a CEX increases protocol centralization because you’re contributing to large staking pools run by these centralized platforms, it is a good option if you aren’t comfortable holding your own keys, or are just getting started in crypto. Many people are clearly taking advantage of centralized staking, as Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance control a combined 30% of staked ETH.
Tactic #2: Hold ETH Derivatives
As more deeply discussed elsewhere in this newsletter, liquid staking tokens are derivatives of ether that depositors receive for staking ETH, and they are called ‘liquid’ because you can enter and exit positions as easily as swapping tokens.
There are a number of staking pools, but we’ll briefly take a look at three liquid staking tokens: Coinbase’s cbETH, Lido’s stETH, and Rocket Pool’s rETH. As we’ll see below, each staking derivative shares a number of common characteristics, but the most common distinction is whether a liquid staking token is rebasing or non-rebasing, referring to whether the rewards come in the form of price appreciation or additional tokens respectively.
cbETH
Coinbase recently introduced cbETH, its liquid staking token. You can buy cbETH on DEXs or you can wrap your staked ETH on Coinbase. cbETH is a non-rebasing token, so it gets positive tax treatment, but the downside is that Coinbase is highly permissioned and centralized, and the cbETH contract has deny-list functionality similar to USDC. While your cbETH earns around 3.25% yield, Coinbase takes a whopping 25% of all staking rewards earned.
Lido
Lido is the OG staking pool, having launched alongside the Beacon chain at the end of 2020. Currently, about 30% of all staked ETH is locked in the Lido protocol. Those who stake on Lido receive stETH in return. Lido provides a centralized staking solution, similar to Coinbase, so depending on your decentralization priorities, Lido may or may not be a good choice.
Unlike cbETH (and rETH below), it’s rebasing, meaning that the price of the stETH should remain pegged to ETH, and additional rewards are paid in stETH. This can create tax consequences, so be sure to know how rebasing tokens are treated in your jurisdiction. stETH currently earns a yield of about 3.8%, but Lido takes 10% of all staking rewards – the lowest of the protocols we are reviewing.
Rocket Pool
Although much smaller than its rivals above, having around 2% of the staking market, Rocket Pool’s rETH is a great option for a liquid staking token, as it combines the non-rebasing characteristics of cbETH with a more crypto-native solution like Lido. But unlike Lido or Coinbase, staking ETH with Rocket Pool is an act of decentralization, as Rocket Pool stakers contribute their ETH to nodes run by individuals, not a centralized set of validators. As we’ll learn below, Rocket Pool provides the smart contract infrastructure for partial node running, and rETH provides ETH to help these partial nodes become full nodes. Rocket Pool is totally trustless and permissionless, which is fantastic, but it does have a couple of downsides. The major downside is that the protocol is still new, so it’s not as battle-hardened as Lido. And while Rocket Pools pays a yield of about 3.6%, it charges a variable fee on non-node operating rewards depending on supply and demand dynamics of node operators and ETH deposited (it ranges between 5-20%).
Tactic #3: Rocket Pool Node
If you want to get a bit deeper into ETH staking but aren’t ready to run a full solo node, Rocket Pool is the protocol for you. Rocket Pool allows users to set up a node with 16 ETH (plus 1.6 ETH equivalent of Rocket Pool’s native token RPL for insurance), with the remaining 16 ETH required to run a full node coming from ETH stakers (rETH holders).
Running a node with Rocket Pool is in line with the ethos of Ethereum, meaning it is totally permissionless and trustless. Rocket Pool nodes are also controlled by individuals, so running a Rocket Pool node helps to further decentralize Ethereum.
To run a node on Rocket Pool, you’ll need hardware similar to running a regular solo node. Yet because of the incentive structure of Rocket Pool, it’s possible for Rocket Pool node operators to earn greater yield than running a solo validator. This higher yield is possible because node operators get 5-20% of the rewards earned by rETH holders in their pools, in addition to regular staking rewards like native yield, MEV, tips, and commission.
Notably, however, each node comes with what Rocket Pool terms an RPL sidecar. RPL is the native-governance token for Rocket Pool, and the tokenomics put a bit of juice into the node operator model, by both providing insurance for rETH holders (RPL can be liquidated to make them whole if necessary) and giving RPL holders rewards in the form of RPL inflation. While rewards for running a Rocket Pool node are currently just shy of 5%, RPL rewards are paid out at greater than 12%.
So just to break it down, there are three ways to earn by running a Rocket Pool node:
Earn standard Beacon chain rewards on the ETH you are staking.
Earn a commission of 5-20% on the pooled staked ETH used to get your node to 32 ETH.
Earn RPL rewards for providing the required collateral/insurance necessary to run a node.
While running a partial node through Rocket Pool isn’t for everyone, for those who are interested in becoming a validator but don’t have 32 ETH, this protocol is a great option to get into the validator game in a decentralized ‘rewarding’ manner.
Final note, Rocket Pool plans to lower the threshold required to run a partial node. Stay tuned!
Tactic #4: Solo Staking
Our final tactic is the Holy Grail of Ethereum staking, running a solo node. To run a solo node, you’ll need to deposit 32 ETH into a staking contract. A full Ethereum node consists of both the consensus layer and the execution layer clients, and these clients make up the software required to verify, attest to, and propose blocks. When you are solo staking, you are responsible for your hardware and uptime. In return for this investment and diligence, solo stakers are rewarded in newly created ETH.
Solo staking is the ultimate goal for many, as it allows stakers full control over their ETH, their staking setup, and ultimately their security. This is all very important, but perhaps the most important aspect of solo staking is that you are contributing to the decentralization and distribution of Ethereum nodes, helping to make the blockchain more secure and resilient.
There are risks associated with running a node. The main risk is that you may be hit with penalties if your node is offline for long periods of time. Your ETH stake can also get slashed for improper validator setup or from bugs in the client software, but these are unusual events. There is a lot of information available about solo staking from the Ethereum Foundation, so I recommend you check out their staking materials if you are serious about wanting to run a full node. While solo staking isn’t for everyone, it’s the best way to help keep Ethereum secure and decentralized.
A quick note: There are also Staking-as-a-Service providers. If you have 32 ETH but don’t want to deal at all with any of the technical complexities or requirements of running your own node, this may be of interest to you. These services run a validator for you, and charge you a small fee in return. Companies that run Staking as a Service platforms include BloxStaking and Kiln. These providers are new, so proceed with caution.
Wrap It Up Like a Token
Where and how you stake your ETH should be something to which you give more than a passing thought. If you choose to stake on a centralized exchange like Coinbase or a centralized protocol like Lido, you’ll be contributing to the centralization of the Ethereum network, while staking with Rocket Pool, running a partial node, or going full-on solo staking helps to keep the network robust and decentralized. The truth is, Lido, Coinbase, Kraken, and Binance control 60% of the proof-of-stake network, so doing a bit more to ensure decentralization is a very worthwhile mission.
But to some people, not having to worry about custody, tax considerations, or access to liquidity is more important than helping to create a more resilient network. Your staking options are as varied as the possibilities on Ethereum — so try out a tactic and join those of us who are staking their claim to the future of the internet.
Actions steps
📖 Read Staking Ether | The Ethereum Foundation
⛏️ Dig into Proof of Stake FAQ | Vitalik
🎧 Listen The Ethereum Merge | Finematics
🎧 Listen ETH Staking Panel | BanklessHQ
🙏 Sponsor: Oasis.app - Borrow Dai & Earn
Project Releases 🎉
Hand-picked articles to understand the current state of the DeFi ecosystem
Arbitrum One is fully upgraded to the Nitro stack
Arbitrum One is now running on Nitro — increased throughput, lower fees, next generation rollup architecture
Some of the improvements include Ethereum L1 gas compatibility, Additional L1 interoperability, and Advanced calldata compression


StarkNet Alpha 0.10.0 released to Goerli
This version is another step towards scaling Ethereum without compromising on security and decentralization
The validate/execute separation provides a protocol-level distinction between invalid and reverted (yet valid) transactions


Starbucks unveils Starbucks Odyssey on Polygon!
A unique experience that enables you to earn and buy digital collectible stamps and unlock new, coveted coffee experiences
This one-of-a-kind loyalty program experience is powered by the low fees and high transaction speeds on the Polygon PoS network


$crvUSD Javascript library
The $crvUSD Javascript library, which will connect a frontend to the smart contract infrastructure, is finally public.
Six things from the codebase that caught attention - LLAMMA, Lending, Liquidations, Swap, Oracle, and Ticks/Bands
Binance.US Launches Ethereum Staking with a 6% APY Ahead of “The Merge”
Binance.US makes staking digital assets easy and accessible by dramatically lowering the barriers to entry
By launching staking for ETH - one of the world’s most widely held tokens - Binance.US is furthering its commitment to always provide customers with the best products and services
https://blog.binance.us/eth-staking/
Chirping Birds 🐤
🔥 and 🧊 tweets from across the DeFi ecosystem








🛠 BANK Utility (BanklessDAO token)
With over 5,000 holders, BANK is one of the most widely held social tokens in crypto. So it bears asking, where are the best places to put our BANK to use? The five protocols below will allow you to deposit BANK in a liquidity pool and earn rewards. To get going, just click on the name, connect to the app, filter by BANK, and start earning passive income.


⚖️ Balancer
Balancer has two 80/20 liquidity pools, meaning that you are required to deposit 80% BANK and 20% ETH in the pool. There is one pool on Ethereum and another on Polygon. Once you’ve provided liquidity, you’ll receive LP tokens. Keep an eye out for opportunities to stake these LP tokens. There is nearly 500,000 USD in the two Balancer liquidity pools.
🍣 SushiSwap
SushiSwap has a 50/50 BANK/ETH pool. As with Balancer, you will receive LP tokens, and while you can’t stake them on SushiSwap’s Onsen Farm yet, you may be able to in the future. Liquidity providers earn a .25% fee on all trades proportional to their pool share. The SushiSwap pool has a little over 100,000 USD in liquidity.
⏛ Rari Fuse Pool
The Rari Fuse Pool allows you to borrow against your BANK or earn huge APY by providing assets like DAI to the pool. At present, all borrowing is paused for this pool. There is over 450,000 USD deposited in the Pool
🦄 Uniswap
The Uniswap V3 liquidity pool is 50/50 BANK/ETH, and provides a price oracle for the Rari Fuse Pool. By depositing in the Uniswap pool, you can earn fees and help enable borrowing on Rari. This pool currently has over 500,000 USD in liquidity.
🪐 Arrakis
You can also provide liquidity to the Arrakis Uniswap V3 pool. The ratio is about 2/1 BANK/ETH. This pool is new, and only has a bit more than $6,000 in liquidity. In the future, you may be able to stake your BANK/ETH LP tokens within the protocol to earn additional rewards.
The Merge Tactics
Beginner Tactics
How to Stake ETH
Author: William Peaster
Liquid Staking Tokens
Author: Ben Giove
How to Win the Merge
Author: Ben Giove
Get Plugged In
Event Highlights
DevCon Bogota—Bogota, Columbia—hosted by the Ethereum Foundation that’s geared toward developers, researchers, and movers within the Ethereum ecosystem. Devcon aims to deliver a holistic learning experience through panels and workshops. This conference is for builders of all kinds: developers, designers, researchers, client implementers, test engineers, infrastructure operators, community organizers, social economists, artists, and more. Oct 11-14 📌 Agora Bogotá Convention Center
ETH San Francisco—San Francisco California—Hailed as the West Coast’s premier Ethereum event of 2022, ETH San Francisco unites blockchain and crypto enthusiasts, as well as developers, industry experts, and tech companies. Discover more Ethereum events around the world here and check out the ETHGlobal site to get more updates about this and other upcoming events. November 3-5, 2022, San Francisco, USA.
🧳 Job Opportunities
Get a job in crypto! Do you like solving hard problems, care about building more efficient markets for everybody, and want to work at the frontier of decentralized finance? Rook is looking for full time contributors, with salaries ranging from $169,000-$722,000. There are positions ranging from engineering, recruiting, product marketing, copywriting, and design. Sound interesting? Sign up for our referral program and go full-time DAO.
Sr. Copywriter (❌ technical)
2D Graphic Designer
Quantitative Analyst
🙏Thanks to our Sponsor
Oasis.app
Oasis.app was born as the frontend to access Maker Protocol and create DAI. It allows you to borrow DAI, exchange your tokens internally and multiply the exposure to your collateral (among the 30 available cryptoassets). Oasis.app is now the most trusted entry point to the Maker Protocol. The long term mission is to allow users to simply and easily deploy their capital into DeFi and manage it in one trusted place.
👉 Get started with the Oasis.app
👉 Follow them on Twitter
👉 Join their Discord