Building Mutable Organizations on an Immutable Blockchain | State of the DAOs
You're reading State of the DAOs, the high-signal low-noise newsletter for understanding DAOs.
State of the DAOs has been discussing DAO tooling since its inception in 2021, and nearly every issue has touched on it in some respect. Why? Because DAO tooling is one of the most challenging aspects of starting, running, and growing a DAO. If coordination is our goal, the tools we use are the means to get there.
Many DAOs have relied on the incumbents to get work done, these tried and tested tools like Snapshot, Sesh, Coordinape, Collab-Land, and Safe. DAOs that do their work on chain tend to use AragonOS or Compound’s Governor Bravo with Boardroom, and some are trying other tooling by Commonwealth and others. Of course these tools have many upstart competitors, but the piecemeal approach to tooling, combined with the immutable nature of the blockchain, has made it so the DAO tooling conversation continues, in nearly every corner of the cryptoverse.
Aragon is the OG DAO tooling platform, helping communities build together since late 2016. This year, they released what may be their most ambitious offering yet - AragonOSx. With this new release, Aragon is bringing flexibly to DAO governance and operations, but more importantly, a mindset that says DAOs work best when they are mutable - that is, when they can respond to changes within the DAO and the ecosystem.
In this issue, Samantha Marin, a BanklessDAO alumni and an emerging leader at Aragon, provides us with the details of this new DAO OS. As she writes "No one can predict what the organizations of the future will look like. So, Aragon has built a completely free and open-source tech stack that anyone in the world can leverage to build their organizations. With the powerful and modular OSx, you can build anything you can imagine! And the simple, no-code front end makes it easy to launch a DAO and start experimenting with governance at the speed of software.”
Whoa.
As always, we conclude this issue with a TL;DR on some of the most recent DAO ecosystem takes and thought pieces, making it easy for you to cut through the noise and learn everything you need to know about the current state of the DAOs.
Contributors: BanklessDAO Writers Guild (Samantha Marin, Warrior, KingIBK, Quilia, Vi-Fi, Tonytad, Kornekt, Trewkat, HiroKennelly, siddhearta)
This is the official newsletter of BanklessDAO. To unsubscribe, edit your settings.
🙏Thanks to our Sponsor
Game7 DAO
Game7 is excited to launch Summon, our novel DAO governance platform.
Summon is a community LiveOps tool that takes governance to the next level by making it easy for DAOs to measure the contributions of their members, and reward them in ways that go beyond money.
How it works: Each community member mints a Soulbound NFT that evolves as the member contributes to the community, making the NFT upgradeable and unique. As each contributor completes quests and tasks, they earn experience points (XP), which help them move up in rank and unlock features and rewards in real time.
By tracking, measuring, and rewarding contributions, Summon provides decision-making capabilities to those who invest time and effort into the community, as opposed to only those who contribute capital.
The result is a meritocratic governance model that distributes power and governing rights to the most productive members of the community.
👉 Sign up to the Game7 waitlist to experience Summon
👉 Follow Summon on Twitter
Building Mutable Organizations on an Immutable Blockchain
How Aragon OSx Took Inspiration From The Early Operating Systems That Revolutionized Computers
Author: Samantha Marin
The blockchain is immutable — you can’t change the past state of anything within it. You can add new entries to the blockchain by signing transactions but you can’t change old entries.
Although this makes DAOs more resilient and transparent, it can be a problem, because they can’t easily change. Like the blockchain, these digital organizations have traditionally ended up being immutable. Until now.
Historically, if you deploy a token-voting DAO on the blockchain, say through an original AragonOS contract or Governor Bravo, you can’t change your mind later and decide to go to allowlist wallet voting, NFT voting, delegated voting, or a new governance model that hasn’t been discovered yet. You’re stuck with what you started with, unless you migrate to an entirely new contract, which is risky, cumbersome, and time-consuming. Depending on the setup of your DAO, it might even be impossible to migrate and evolve!
But if there’s anything we’ve learned in the past seven years of DAO evolution, it’s that organizations must be able to adapt and change. If organizations can’t experiment and evolve, they will fail.
Aragon set out to solve this problem by powering every DAO with an evolving permission management system.
But before we get into that, let's talk about operating systems.
What’s an Operating System?
An operating system is what makes your computer run. Mac OS, for example, is the operating system that all Mac computers use. The operating system acts as the intermediary between the hardware and software of your computer. It operates as a permission management system, essentially allowing programs (apps you install on your computer) to run by granting permissions to them. You can have multiple apps on your computer at once, and when you don’t need an app anymore, you uninstall it.
This feels completely normal to us today, but we’ve come a long way.
In the early days of computers, each program was the entire system. You couldn’t run multiple programs at once. Computers were built with a single program in mind. There was no way to install a new app or program — you had to reprogram your entire system to do so. Not to mention that these computers were the size of refrigerators and not very practical.

Qualities of computers in the 1970s:
A single program was the entire system
One program for every architecture
Not possible to install programs (you would need a new architecture for that)
To edit it, you need to reprogram the entire system.
A New Paradigm in Operating Systems: Linux, Mac OS, and Windows
Then came operating systems like Linux, Mac OS, and Windows. These were revolutionary because of their adaptability. You don’t need to update the entire system to make a change: you simply update the app.

A modern operating system works like this: there is a trusted kernel at the center with unrestricted resource access to tools like the camera, microphone, screen, and disk. The kernel is the central component of the operating system and has full control of hardware systems.
Then, there are several untrusted programs that request access to the shared resource. A program might be Google Chrome, the Mail app, Discord, or any other application you install on your computer.
Every app you install needs permission from the operating system to function, and, depending on the permissions you have set up, it succeeds or fails.
In short: operating systems manage permissions to untrusted apps.
For example, when you install Discord, you need to give it permission to access your camera and microphone. However, you can choose to block access to these tools.
With an operating system at the core, there’s no need to reinstall the entire OS to make one update in an app. You simply update the app itself.
This was revolutionary for the development of more advanced applications. Without operating systems, we wouldn’t be able to do anything that we can with computers today.
The DAO Frameworks on Blockchains Operated Like Early Computers
Blockchains are a paradigm shift in so many ways. But the original DAO frameworks on top of them operates much like those refrigerator-sized computers of the 60s and 70s.
To edit a set of smart contracts you’ve deployed on the blockchain, you need to reinstall that entire deployment. This makes development slow, opens up security risks, and makes developing smart contracts very high stakes.
Redeploying a contract whenever it needs an update is also expensive, because you need to pay gas fees every time you add a new state into the blockchain.
DAO frameworks on blockchains today:
are like the original computer programs before operating systems
need to code and redeploy custom contracts to get what your community needs — there’s no way to easily install and uninstall new features.
The Problem: Organizations Struggle To Adapt on an Immutable Blockchain
DAOs struggle to adapt because they need to update their on-chain deployment every time a major change — like altering their governance structure — is made.
Let’s go through Aragon’s approach to building OSx and the entire stack on top.
The Solution: Build an Operating System For DAOs
When building OSx, Aragon took the approach of trusted kernel plus plugins — just like the operating system that revolutionized the computer.
The plugin is a smart contract external to the DAO that can do things on behalf of the DAO only when permissions are granted.
The DAO vault, or treasury holding all of the DAO’s assets, is the trusted kernel at the center. For plugins to interact with those assets — such as to withdraw, swap, or stake — they need to be granted permission.
The plugins can be untrusted, meaning it doesn’t matter who builds them or what they contain. This is because the plugins aren’t baked into the DAO itself with full permissions to the vault; they’re external to the DAO’s vault, just like applications are external to a computer’s operating system.
This means the plugins can also be “unplugged,” or have permission revoked. This is similar to uninstalling an app on your computer.
Every DAO is a permission management system at its center, managing how the vault, which can contain assets or other information, is accessed. This permission management system is what grants and revokes permission to the external plugins.
The Aragon OSx protocol was built with the UNIX philosophy in mind: small, composable building blocks that can be rearranged into many different types of organizations. DAOs will mix and match plugins to build any type of logic their DAO needs.
In the image below, you can see the assets in the DAO’s treasury, like ETH and DAI. A layer of permissions separates those assets from the plugins below, which need to request access from the DAO to interact. So, in order for the “withdraw” function to execute, it needs to go through the permission layer.
Developers can choose how they want to design their plugins. The plugins can be upgradeable, making it easy to change and install new versions. Or, they can be immutable, so they’re not changeable later on.
Much like the apps you use on your computer and phone, developers are in control of how they design plugins. Aragon is providing the operating system and the basic functions DAOs need to operate, but builders like you are expanding applications and functionality on top!
Oracles: Permission Filters to Bring More Precision to Permission Management
We can take DAO permission management one step forward with oracles, which are like permission filters. An oracle “talks” to the blockchain to give it information from the outside world. For example, a blockchain can’t know what the price of gold is. So if you wanted to tokenize gold on-chain, you would need an oracle to constantly tell your contract what the price of gold is.
DAOs can use oracles to make their permission management more specific. For example, a DAO might want to grant permission to swap tokens on the Uniswap plugin, but only if the transaction is under $5,000 in value. The DAO would use an oracle to add logic to the plugin, basically customizing it to the DAO’s unique needs.
Oracles could become a key part of many plugins in the future.
How to Access the Power of Aragon OSx
There are a few ways to tap into the power of Aragon OSx for your DAO. Aragon has built a tool for every type of builder.
For No-code Builders: Aragon App
Aragon App: the no-code front end to Aragon OSx. Build a DAO in minutes without writing a line of code. The Aragon App is built with user experience first.
For Engineers: Aragon OSx
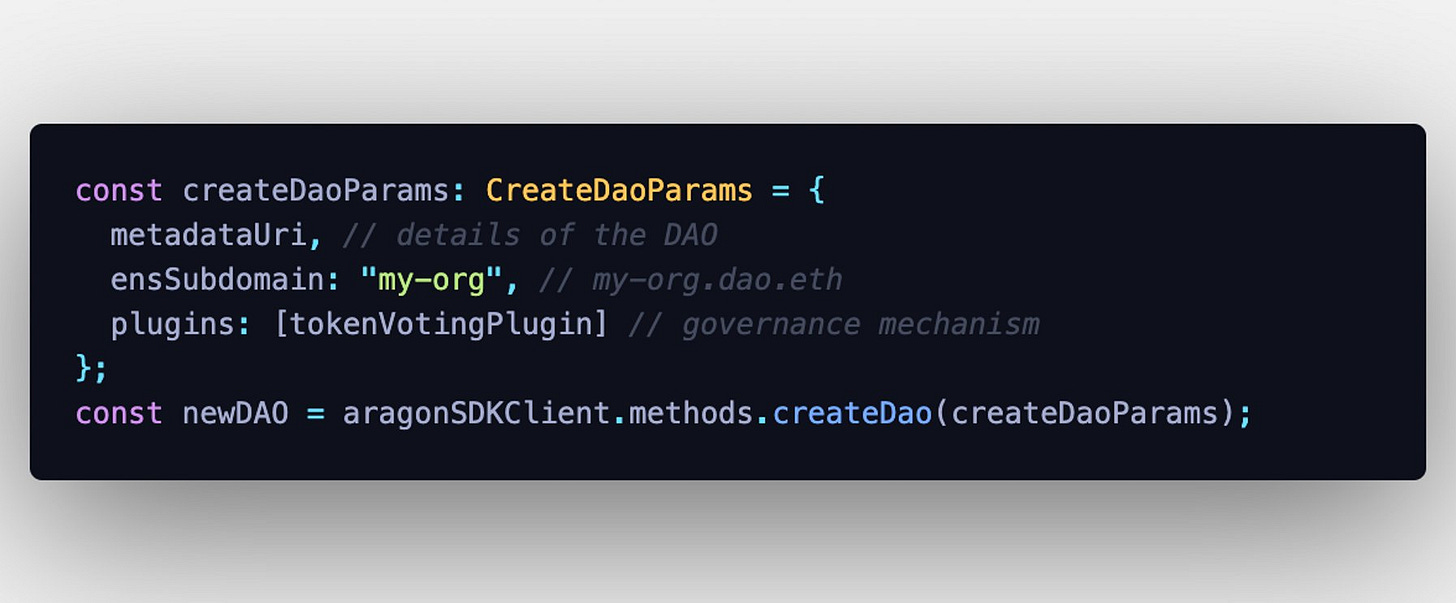
Aragon OSx: You can build a fully custom DAO with Aragon OSx by installing the plugins you need, and even creating your own! Aragon OSx includes an SDK, allowing you to deploy a custom DAO with just a few lines of code. You can use Javascript, so no need to be a Solidity engineer to use the SDK. The Aragon SDK is framework agnostic and we’ll be launching clients for other programming languages in the future. Check out the developer portal to get started.
Enabling Organizations We Can’t Yet Imagine Today
No one can predict what the organizations of the future will look like. So, Aragon has built a completely free and open-source tech stack that anyone in the world can leverage to build their organizations. With the powerful and modular OSx, you can build anything you can imagine! And the simple, no-code front end makes it easy to launch a DAO and start experimenting with governance at the speed of software.
We don’t have the answers, you do. We create tools to help you build the new forms of organization and coordination the world so desperately needs.
We can't wait to continue building better, together.
Start building your DAO and claim your dao.eth subdomain on the Aragon App today! Or, stay in touch by subscribing to our weekly newsletter and following us on Twitter and Lens.
Samantha is the Content Editor for the Aragon Growth Guild and the writer of the Quorum newsletter. She got her start in web3 in the Writers Guild at BanklessDAO.
Actions Steps
📖 Read Updating the DAO Operating System | State of the DAOs
⛏️ Dig into DAOs, DACs, and On-chain Org Design: A DAC Manifesto | 0xJustice
DAO Spotlight: Game7 DAO
Game7 is a community formed to accelerate the adoption of Web3 gaming through crowdsourcing, to create public goods that can be owned by many. It’s a home for those who seek to influence, shape and build a better gaming industry, where the interests of developers and players are aligned.
Communities are formed through shared missions, experiences and support. Game7 operates much like a collaborative game. A member’s actions and contributions are measured to unlock influence.
Game7 prioritizes steady growth over short-term profit, enabling teams to maintain focus on building and real impact. The DAO aims to invest its treasury in infrastructure building, tool acquisition, development of the community, and gaming.
The community actively supports open-source software. They created a grants program to fund open-source software development; a way to encourage builders to focus on building without having to worry about funding (or anything other than building). Game7 does not expect financial returns as this is their way of supporting public goods.
Organizing global events so people can connect and collaborate is very important to Game7. The events could range from academic conferences to annual summits and pop-up online events conducted both digitally and in real life.
Game7 recently launched Summon, a tool that allows DAOs to measure the contributions of members and reward them in ways that go beyond money: status, rewards, influence, power. Summon intends to provide a contemporary solution to modern DAO governance by progressively rewarding those who contribute. Summon is a meritocratic governance model and it can integrate with any existing management tool stack. Visit their waitlist and click “Join Now” to sign up for the Game7 community prototype.
Game7 believes everyone has something unique to offer. You can join by organizing initiatives, collaborating with like minded individuals, and building products that benefit everyone.
Join the Game7 community by visiting their Twitter and Discord.
Ecosystem Takes
🔥 and 🧊 insights from across the DAO ecosystem
Governance and DAOs
Author: Polynya
🔑 Insights: There are inconsistencies about whether DAOs or the traditional models serve the goal of decentralization or public ownership better. It is not impossible for traditional organizations, such as cooperatives, to use blockchain and smart contract technologies to become more efficient. This questions the necessity for creating DAOs.
One of the main self-inflicted setbacks that DAOs battle is adopting the rudimentary methods of organization. There are three suitable models for DAOs to emulate — public companies, local governments, and cooperatives. Each of these models are dependent on the type of protocol in use.
DAOs may also thrive more in systems that employ flat meritocratic structures coupled with layered management where needed.
Another effective prospect for DAOs is cooperatives. The key to this system is that instead of plutocratic token-gated voting, there will be a democratic one-user-one-vote by builders in the community.
Regardless of the experimentations with the different DAO models to improve democratization of ownership, a DAO is still in need of a functioning and efficient organizational structure.
Solving The DAO Data Problem
Author: Traver Normandi
🔑 Insights: Identity and decentralized social graphs enable DAOs to improve their data and workflows. New on-chain tools are helping DAOs collect detailed data beyond the range of web2 organizations and current DAO tools.
Acquiring information can be difficult due to a lack of infrastructure, admin permissions, and incompatible data across platforms. An on-chain DAO stack would allow composable applications to leverage one core database: the blockchain.
On-chain identity uses a single credential to deliver a user’s on and off-chain identity across the entire DAO tool stack. After its regularization, DAOs can adopt these identities to wield authority amongst valued stakeholders.
On-chain transactions create data layers used by DAOs as leverage between contributors and the organization. This enables transparency and obliterates information asymmetries, making DAOs accountable.
As a result of the on-chain governance cost, data solutions that transmit identity across on-chain and traditional web2 rails are currently being worked upon.
Multiplayer Creation: Unlocking Participatory Media
Author: 1kx.eth
🔑 Insights: Working in isolation while trying to satisfy the artistic needs of an audience has been the norm for creators. But with the emergence of web3, they can have a community participate in the creative process by connecting with individuals that align with their values, sourcing ideas within the community, and obtaining constructive feedback that could guide future projects.
Multiplayer creation is the transformation of the creative process enabling multiple individuals to participate in one or more stages of the creative work.
The individuals involved in this process participate in either of these stages: formation, coordination, production, value distribution, or post-release.
Multiplayer creation tools can transform a consumer into a creator and increase the quality of art released as it encapsulates the creativity of different individuals — turning on-chain interactions into a form of self-expression.
Hyperstructures
Author: jacob
🔑 Insights: Hyperstructures are crypto protocols that can run for free and forever, without maintenance, interruption, or intermediaries. They are free, unstoppable, permissionless, expansive, valuable, and credibly neutral. Builders and participants are also rewarded for creating and contributing to a Hyperstructure that serves society for many years.
Creating ownership and governance in Hyperstructures should only be done where it is absolutely necessary.
Hyperstructures are created to power not just one interface, but millions of interfaces.
With web3, we can restructure the utilities of the internet of the past 40 years outside of private control, and create entirely new ones that seemed impossible before.
For the sake of progeny, we must create Hyperstructures in their purest, most free, and most beautiful forms.
Progressive De/Centralization: A Playbook for Building Decentralized Applications
Author: kydo
🔑 Insights: Progressive decentralization is becoming increasingly popular in the crypto industry, though concerns have been raised about its efficacy. This playbook introduces a set of actions that builders can use to promote decentralization without directly breaching legal standards.
The initial step is creating a protocol and product allowing contributors to give feedback without the hassle of regulatory challenges.
It is also necessary to formalize the protocol development procedure and give the protocol foundation ownership.
The product development process should be organized in the manner of a traditional business.
A token might be introduced to manage the protocol development process.
🙏 Thanks to our Sponsor